Commercial, Residential, and Industrial Buildings (Non-Point) #
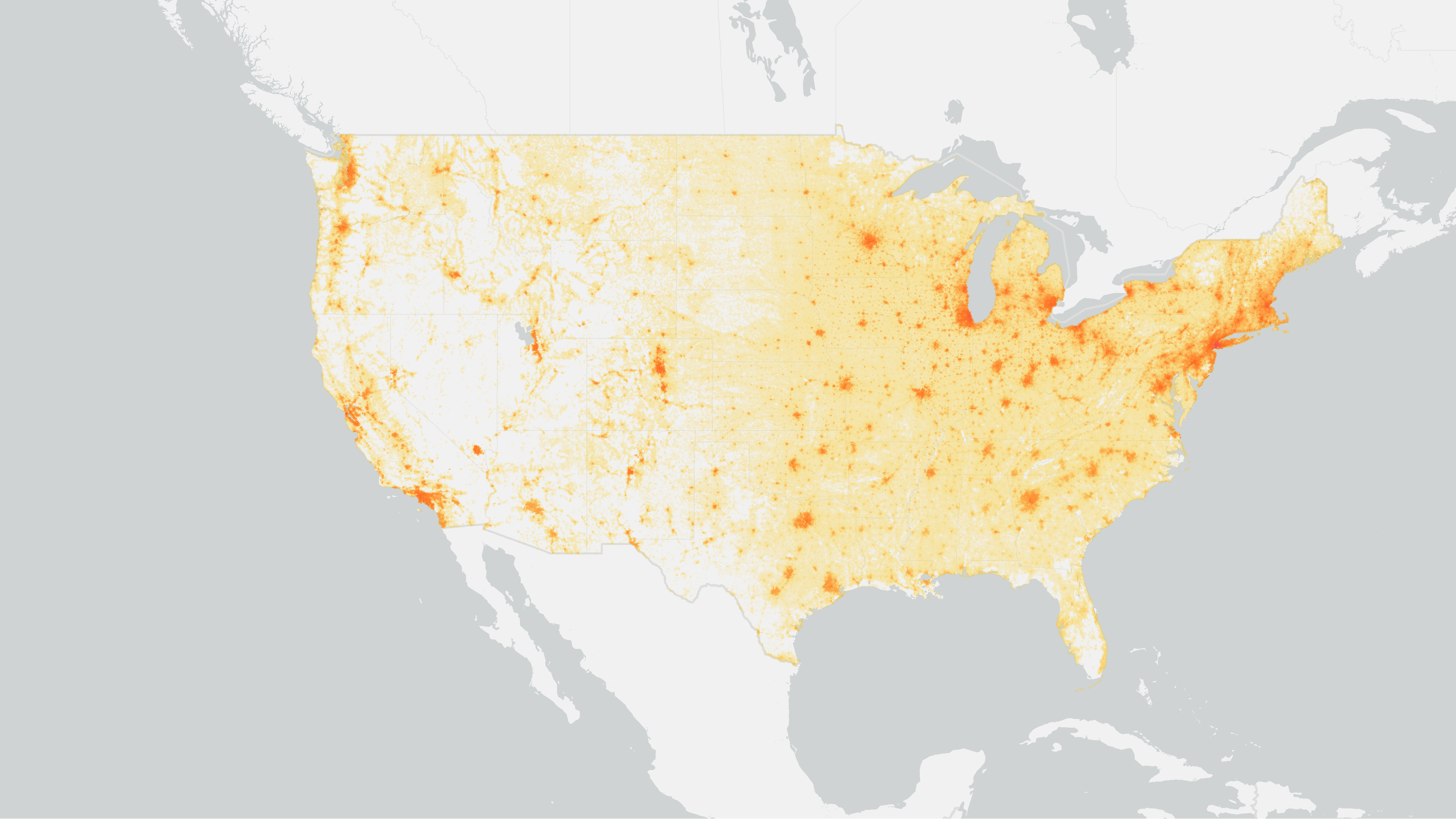 The buildings sector returns point-level CO₂ emissions estimates for industrial, commercial, and residential buildings in the US based on nonpoint NEI CO data and NSI building surveys.
The buildings sector returns point-level CO₂ emissions estimates for industrial, commercial, and residential buildings in the US based on nonpoint NEI CO data and NSI building surveys.
Commercial, Residential, and Industrial Buildings (Non-Point) Sector Definition #
We define the Buildings emissions sector as a subset and downscaled version of the NEI nonpoint emissions. The NEI nonpoint emissions represent the large number of diffuse, small (<25,000 MTCO₂e) carbon emitters associated with industrial, commercial, and residential activity, such as commercial cooking emissions. We define the industrial, residential, and commercial buildings based on the EPA’s level-2 source classification codes (SCC) definitions.
Commercial Buildings (Agriculture Equipment) #
Emissions from agriculture equipment are estimated using county-level CO₂ emissions from NEI Nonpoint emissions data.
Commercial Buildings (Agriculture Equipment) Sector Definition #
Agriculture equipment is defined using key words in the level-2 SCC definitions in the NEI.
Industrial Buildings (Stationary Point) #
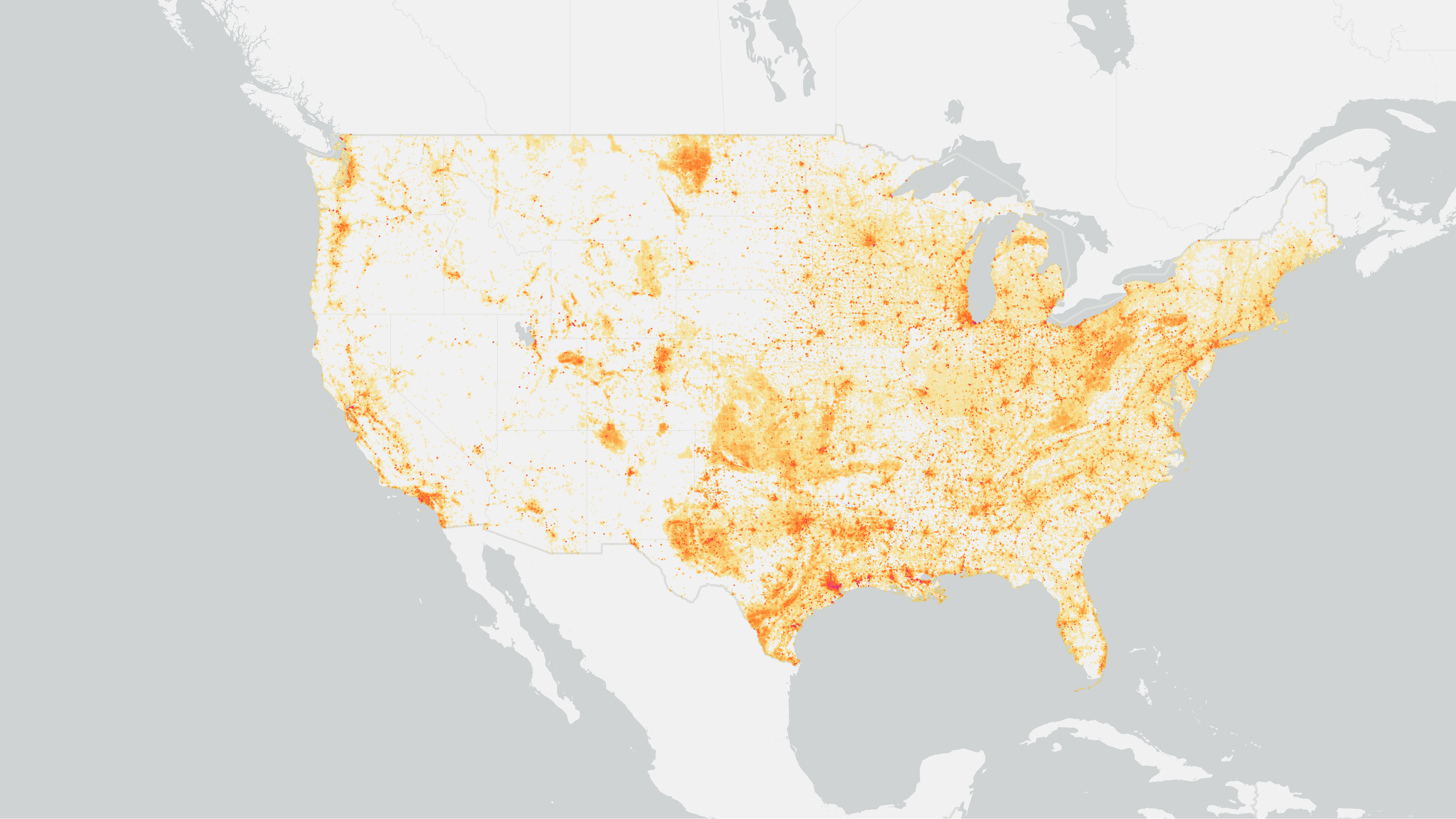 The stationary point sector returns point-level emissions representing large CO₂ emitting facilities using data from the Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program (GHGRP) and US EPA Envirofacts.
The stationary point sector returns point-level emissions representing large CO₂ emitting facilities using data from the Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program (GHGRP) and US EPA Envirofacts.
Industrial Buildings (Stationary Point) Sector Definition #
The stationary point sector encompasses facilities that emit greater than 25,000 metric tons CO₂e per year (i.e., large CO₂ emitting facilities), which are required to report emissions to the EPA. These facilities encompass the direct emissions from fossil fuel combustion and process emissions from the activities defined in Envirofacts.
Industrial Buildings (Oil & Gas) #
Emissions from Oil and Gas are estimated using county-level CO emissions from NEI Nonpoint emissions data and emission factors to convert to CO₂. Emissions from this sector are generally from the combustion of fossil fuels used in upstream and midstream oil and gas exploration and production. Examples include artificial lift engines, pneumatic pumps, well heaters, compressor engines, and flaring. Emissions from refineries and other large facilities are included in the industrial facilities (stationary point) sector.
Industrial Buildings (Oil & Gas) Sector Definition #
Oil & Gas is defined using key words in the level-2 SCC definitions in the NEI.
Emissions data sources #
- NEI Nonpoint
- EIA SEDS (2021 Version)
- NSI
- EPA Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program (GHGRP) (Annual)
- GHGRP (Subparts E, S, BB, CC, LL)
- Envirofacts
Methods summary #
The industrial buildings sector is comprised of non-point industrial buildings, point industrial buildings, and oil and gas. The buildings sector method estimates point-level CO₂ emissions for industrial, commercial, and residential buildings by combining NEI nonpoint CO data, EIA SEDS fuel consumption data, and NSI building surveys. NEI data is filtered for CO emissions and downscaled using building square footage, with CO₂ estimates calculated via emissions factors. For counties with zero or inconsistent emissions data, state-level CO₂ emissions are backfilled using building square footage and adjusted based on state fuel consumption ratios. The stationary point industry sector method aggregates CO₂ emissions data from large facilities using EPA’s GHGRP and Envirofacts datasets, focusing on facilities emitting over 25,000 metric tons CO₂e annually. Data is prioritized by GHGRP Annual, followed by Envirofacts and GHGRP Subparts, with fuel consumption estimates calculated where fuel data is missing. Emissions are self-reported, and no emissions factors are applied. Projections for future emissions are calculated using state-level and composite fuel consumption estimates. For stationary point Oil and Gas sector estimates county-level CO₂ emissions using NEI nonpoint data, with emissions categorized based on SCC level definitions for oil and gas exploration and production. Emissions factors are applied using data from the EPA Nonpoint Oil and Gas Tool, with adjustments made for state-specific variations and manually compiled emissions factors for certain activities. Emissions are aggregated by fuel type, state, and county, and temporal interpolation and projections are applied as needed.